When managing databases became too complex, developers built cloud solutions that could make databases easier to manage and handle. The same thing is happening with the backend as backend development becomes more complex. Companies are building services that provide backend functions for developers.
We term these services backend-as-a-service (BAAS). Appwrite is a good example of a BAAS. This piece of writing is about Appwrite, including why it exists, how to install it, the services it provides, and a comparison of Appwrite with other backend solutions.
What is AppWrite?
According to appwrite.io,
Appwrite is a self-hosted backend-as-a-service platform that provides developers with all the core APIs required to build any application.
This means that appwrite provides backend features or services that you can integrate into your frontend or mobile application. Appwrite provides these services for your application, irrespective of the programming language or operating system the program is running on.
Appwrite is popularly called the Firebase alternative. Firebase is a backend solution owned by Google. Appwrite prides itself on being open-source, with a large community of developers, and believes itself to be the developers' favourite.
Note: I did this tutorial using Windows, so most of the commands are for Windows.
Why Appwrite?
- Appwrite provides all the backend features that you need to get your application running.
- You can use appwrite with your custom backend application for an optimum experience as well.
Appwrite saves you the cost of having to maintain a server.
Appwrite provides a database as well, sparing you with the hassle of creating and managing a database.
- Appwrite takes away the long process of having to learn a new language just to build a server. As it is language-agnostic, developers can run it in any language they wish.
How To Install AppWrite
Appwrite uses Docker containers to run, so to install appwrite, you need to install Docker Desktop.
If you are using Windows, you will need to install Linux before you can use Docker. So follow this link to install the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2. Afterwards, you can install Docker Desktop.
After installing Docker Desktop, open Windows PowerShell and enter this command:
docker run -it --rm `
--volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock `
--volume ${pwd}/appwrite:/usr/src/code/appwrite:rw `
--entrypoint="install" `
appwrite/appwrite:1.0.3
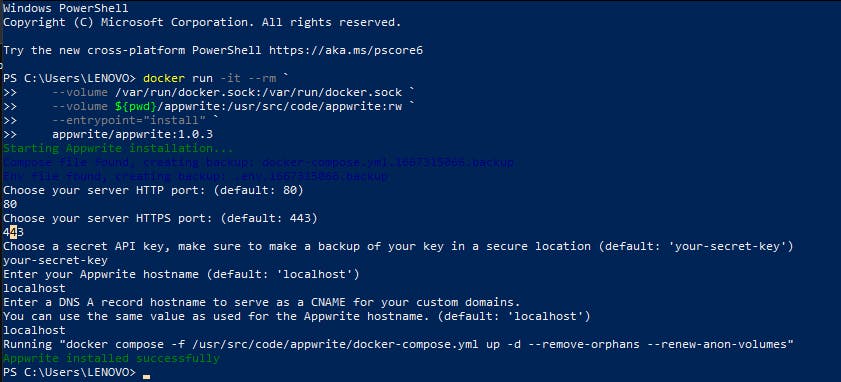
You can follow this link to install it either on the command line or on Unix.
Appwrite is installed successfully so open docker you should see the appwrite container.
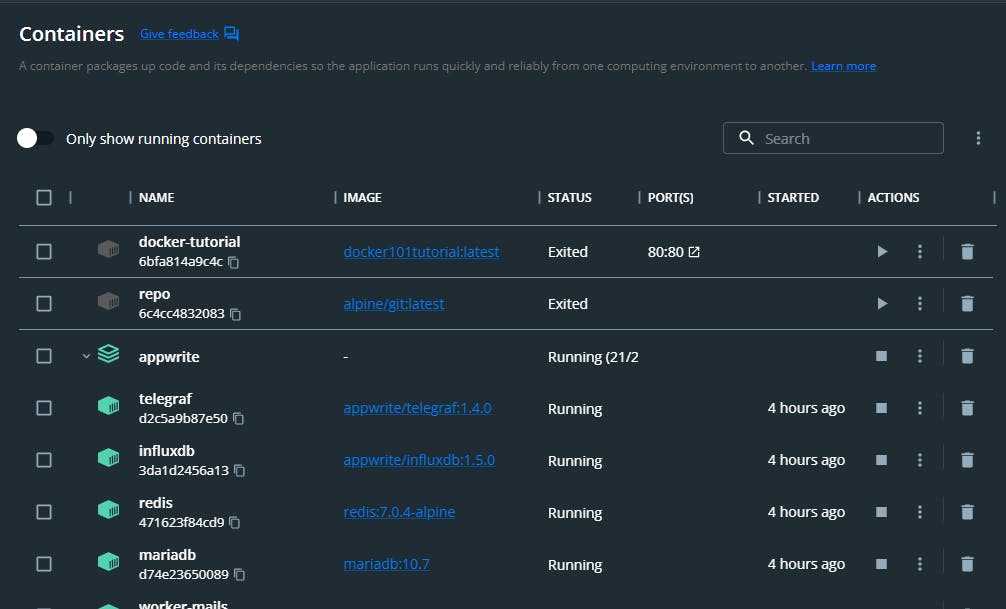
To view appwrite on a browser, scroll down to the traefik container and click on any of the links.
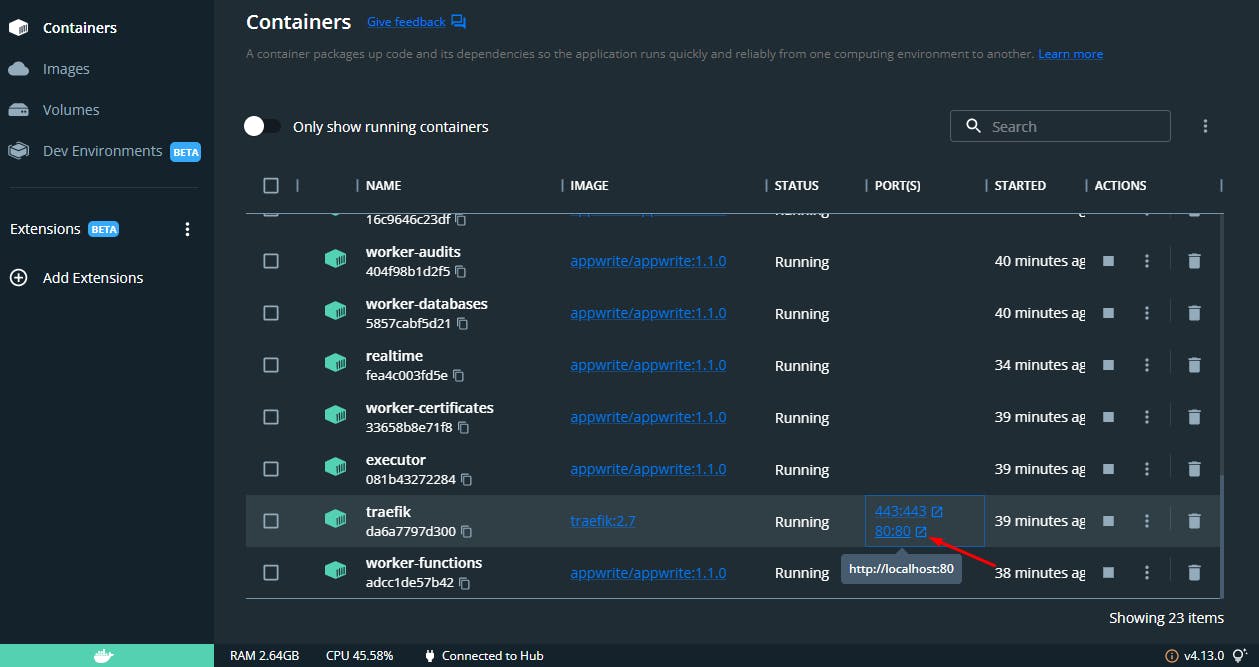
That will open on your local browser and you should see the appwrite UI.
Fill in your details and click on sign up
After registering, go back to the docker container and click on the same link again.
This time around, it will prompt you to sign in.
Sign in and it will take you to the appwrite dashboard.
Then you can begin to create projects.
Appwrite services
Appwrite offers services such as
Creating and managing databases With this service, you can perform database functions like read, write, and update and you can also query your data.
Storage This service allows you to record, store and delete files.
Users' authentication and authorization With this service, you can grant authorized access to your users. You can limit your users from accessing information you wish to keep out of their reach.
Use of webhooks Appwrite provides the use of webhooks. Which lets you connect your client app to receive requests from appwrite for events that you register for.
API Keys Appwrite also provides an API key that you can use to perform API requests and make your client app functional
Task management Appwrite manages your tasks for you, sending you notifications of relevant updates.
How to create a database on Appwrite
To create a database on Appwrite, you must create a project first.
- Click on the
Create a projectbutton.
- Name your
projectand name yourproject-idtoo and that would create a new project.
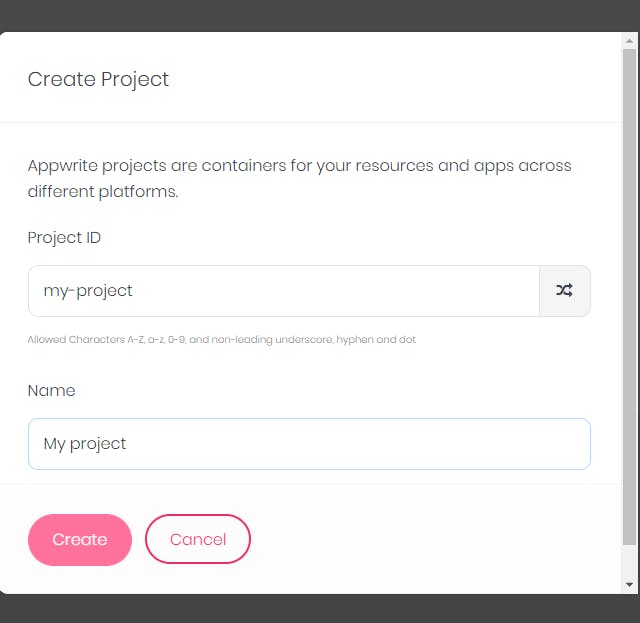
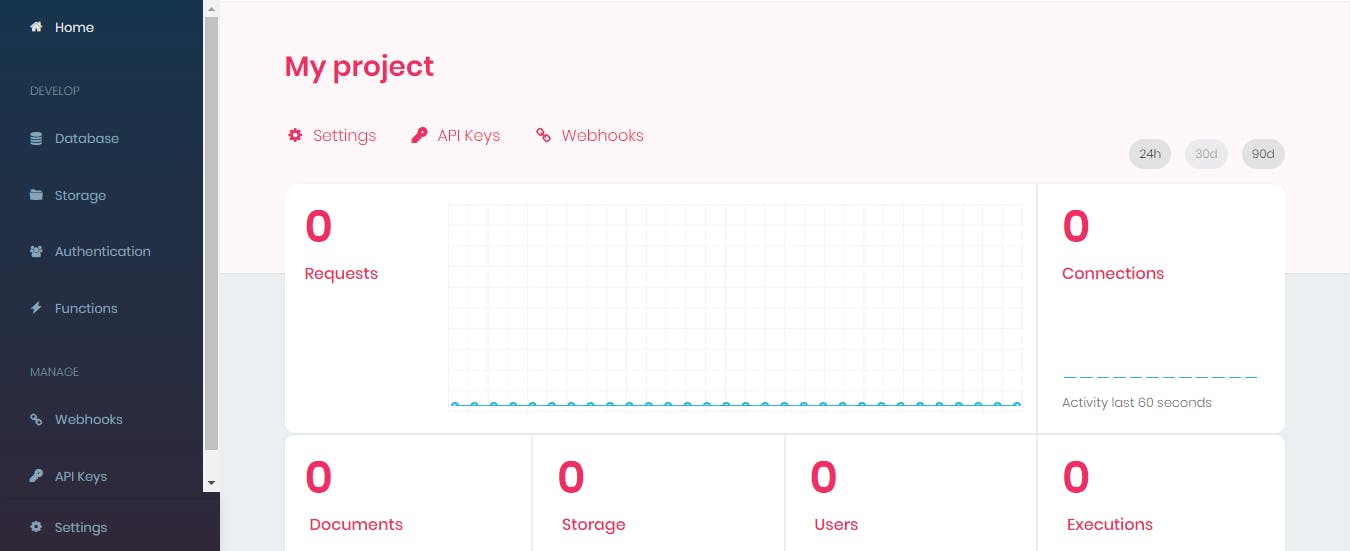
- After creating the project, then you can create a new database by clicking on the
databasebutton.
- When you click on the database, it will open the database section where you can create a new database.
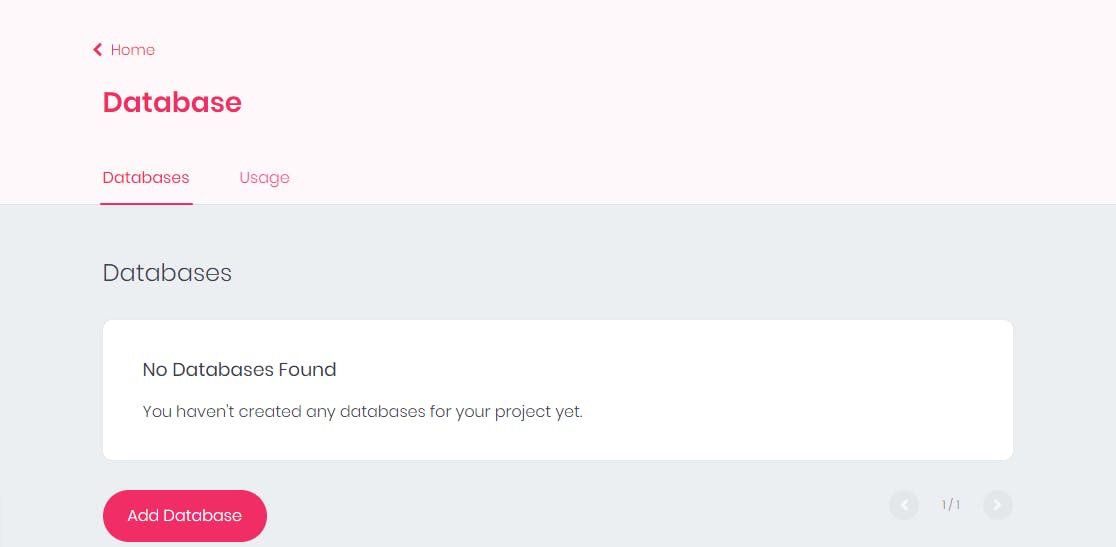
- Then Click on
Add Database, so you can create a new database.
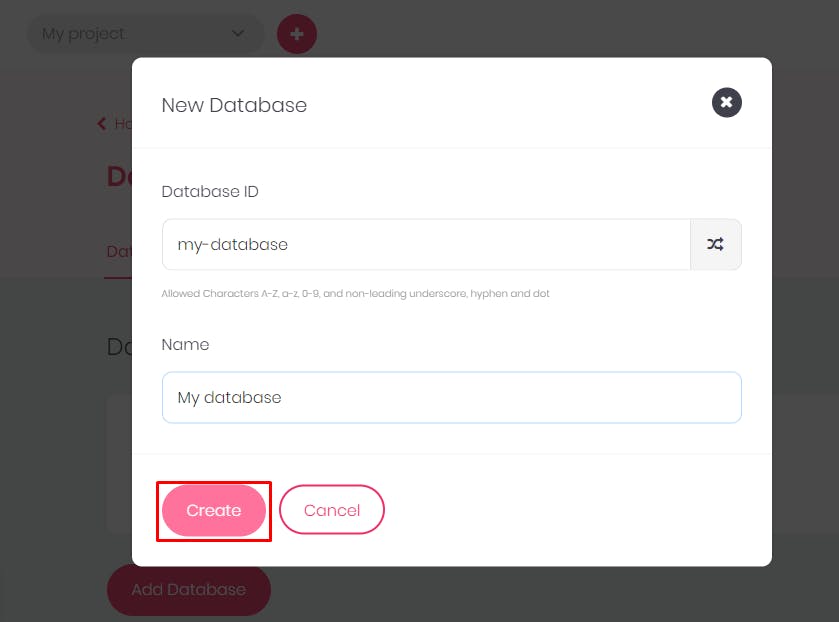
Enter the name of the
databaseand thedatabaseidand then click onCreateThat will create a database for you.The next thing would be to create a collection. A collection is a compilation of documents with the same structure. A collection will contain options like attributes, indexes, and documents for the database you created.
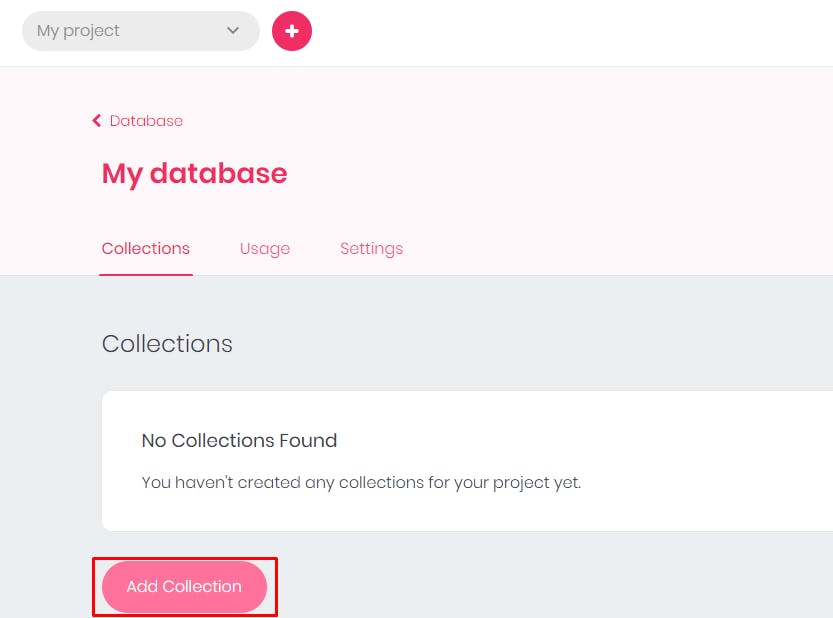
- Name your
collectionand yourcollectionidand click onCreate.
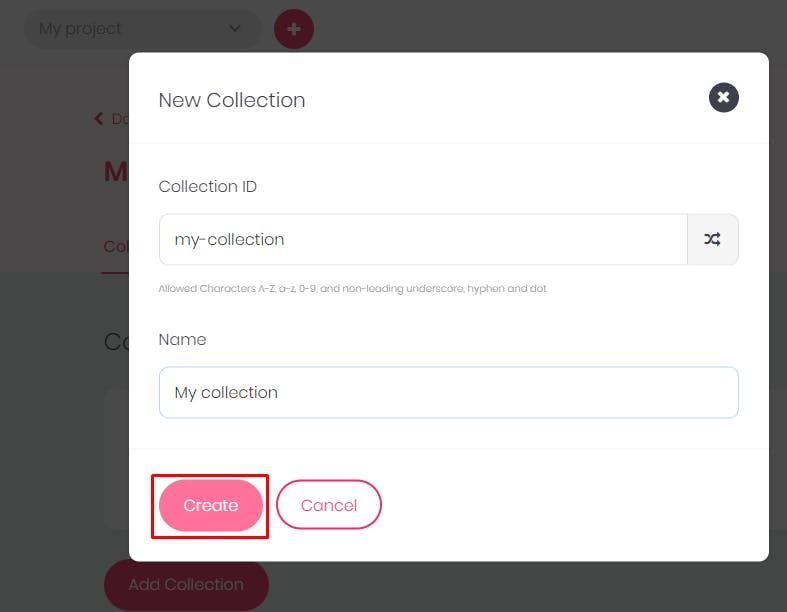
That would create a collection for you.
- Enable permission for the users or members you would allow.
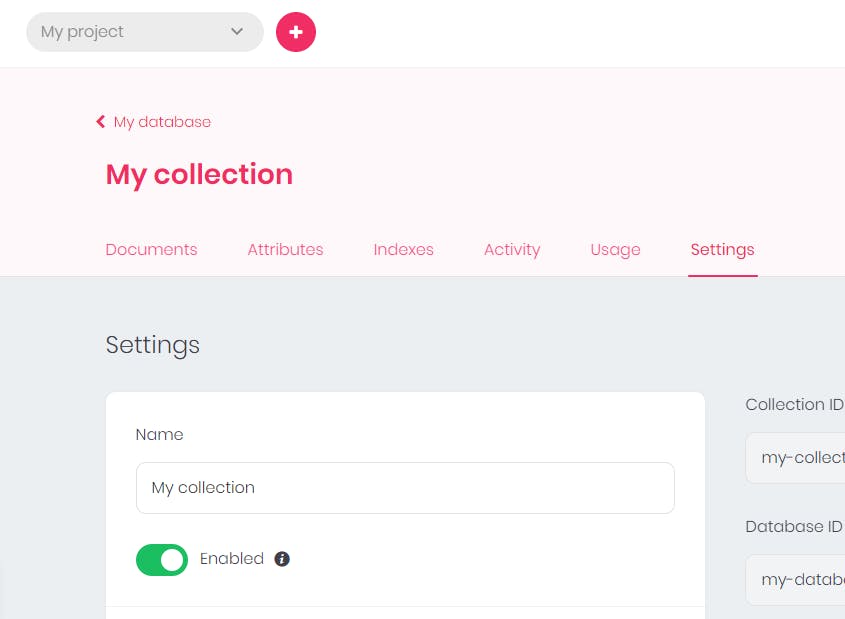
- Click on the
Add Rolebutton and select the users or members you allow. You can also assign the operations they are to carry out. For the sake of this tutorial, I will add only one role.
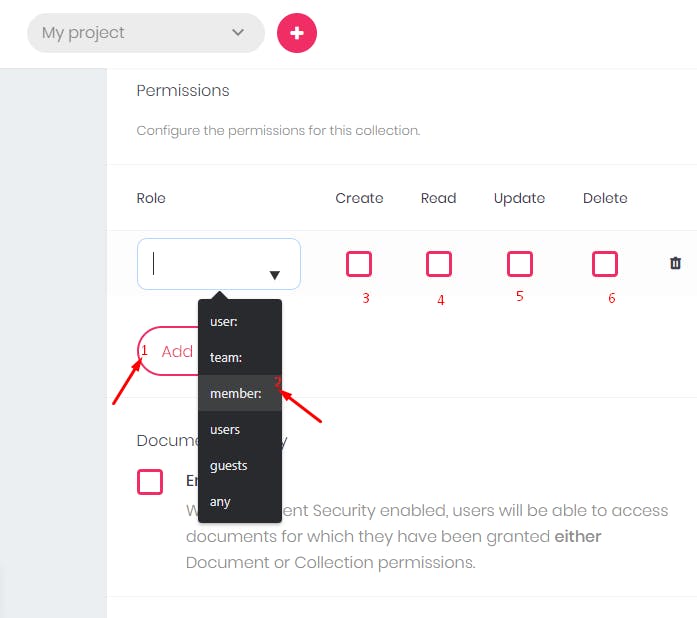
- After that, you can enable permission for the documents, which will grant your users access.
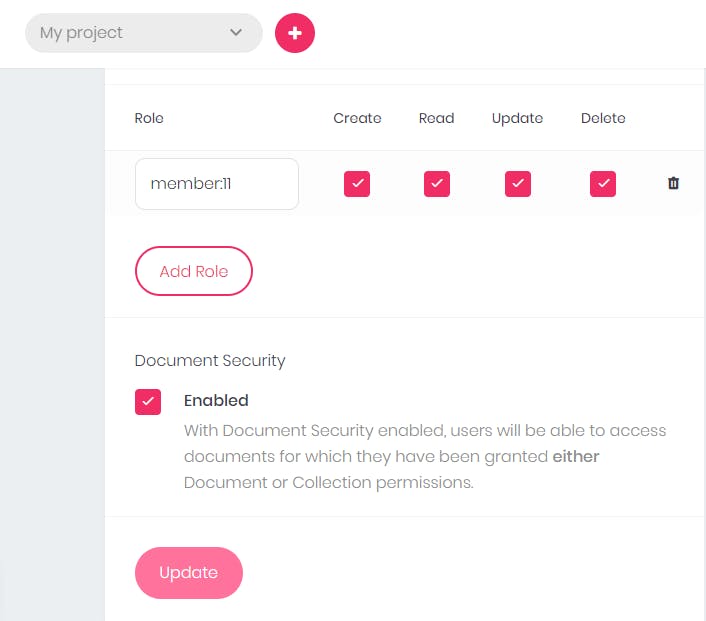
Click on
Updateto update the changes you have made.After that, you can add attributes.
An attribute will be used by the Appwrite API to validate your users' input. It will also define the structure of your document.(Source: Appwrite documentation)
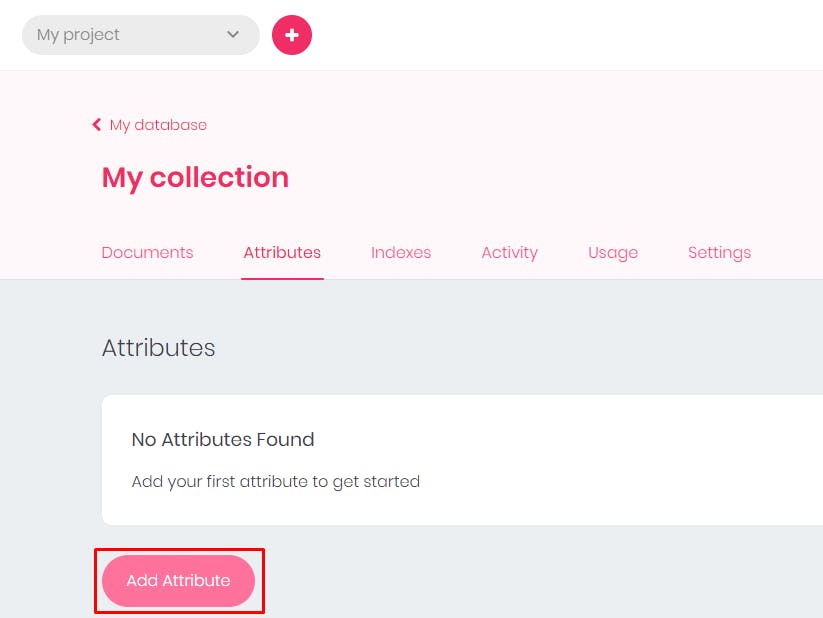
Click on the Add Attribute button to add attributes.
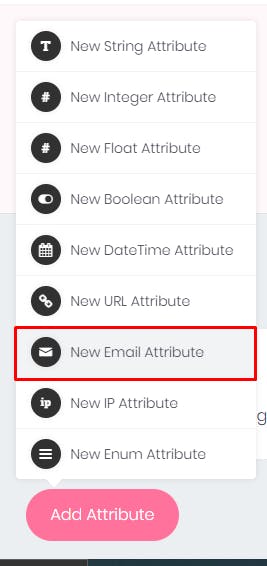
- I will select the email attribute for this tutorial, you can choose an attribute you need.
- Name the
attributeidand give it a default value if you do not want to make it required. I will give it a default value ofmymail@mail.com
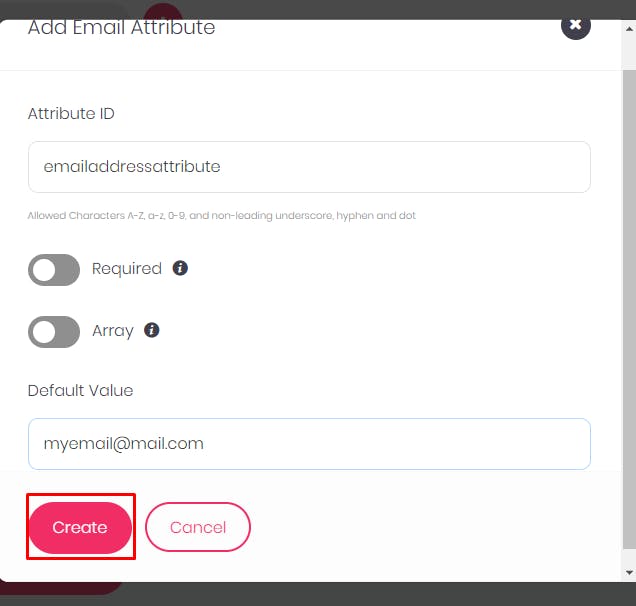
When you click on
Create, it will create the email attribute. The next thing would be to create documents.Click on
Add Document, and that will bring up a prompt.
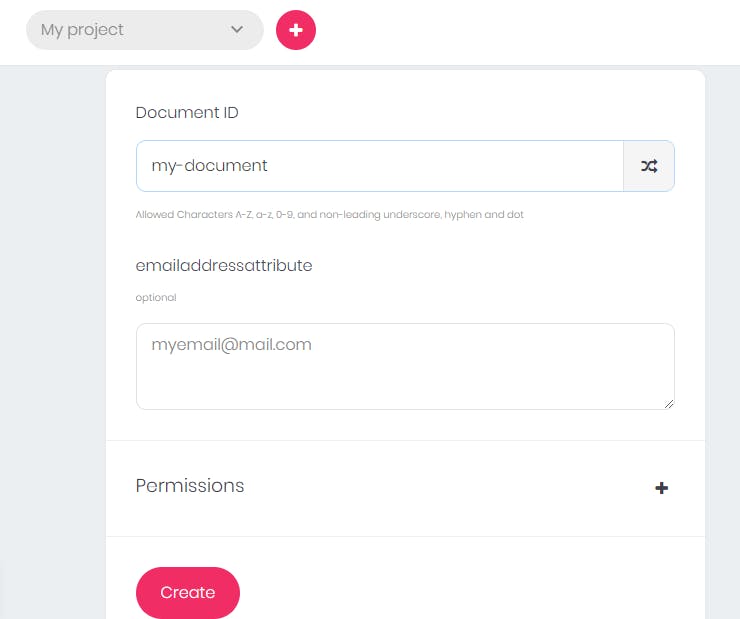
- Name your document, grant permissions, and click on
Create, which will create the document.
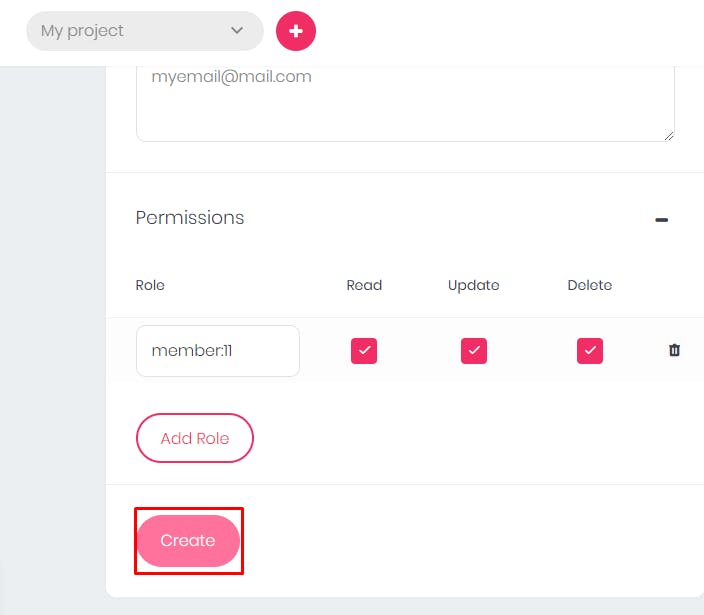
- After adding the permissions and clicking on
Createthat will create the document.
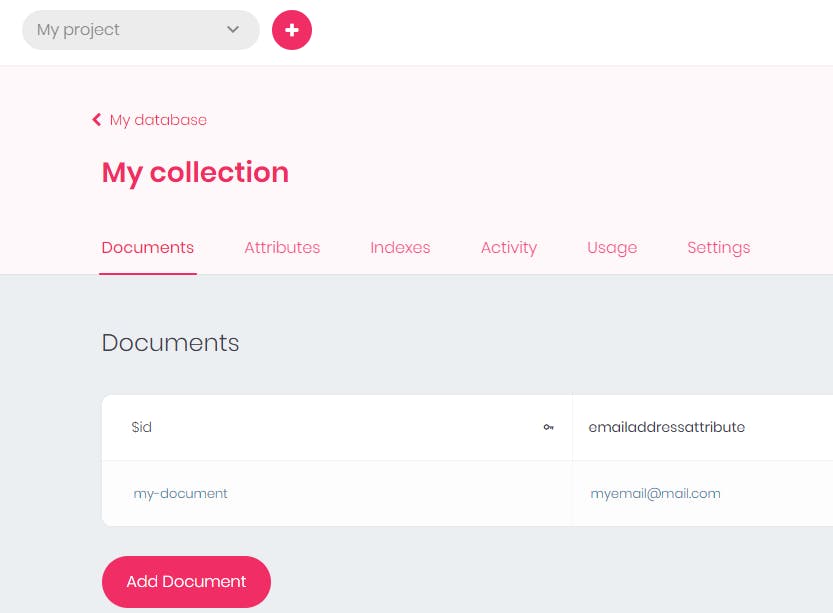
The document has been created. That is how to create a database for your project on appwrite.
Appwrite vs Firebase
Appwrite and Firebase are both BASS and they offer the same services but there are some differences between them.


| Appwrite | Firebase |
| Provides MySQL and NoSQL database | Provides NoSQL database |
| Self-hosted and open source | Hosted on Google’s cloud |
| Tedious set-up process | Easier to set up |
| Free access to an unlimited number of projects | Provides free access to a few projects |
| Open source | Backed by Google, a private entity |
| Has a large community of developers and is open to all | Access to google developers |
Appwrite vs Nhost


Appwrite and Nhost are BASS too and they are both open source and see themselves as the Firebase alternative. However, there are some differences between them.
| Appwrite | Nhost |
| Uses MySQL and NoSQL databases | Uses PostgreSQL |
| Uses Docker | Uses AWS |
| Free, for now, | Offers paid packages on their cloud version |
| Does not use the Hasura framework | Uses the Hasura framework |
| Uses REST APIs | Uses GRAPHQL API |
| Self-hosted only | Self-hosted and hosted on the cloud |
Appwrite vs Supabase

Appwrite and Supabase are BASS and they share so many similarities. They are both open source, they use the same REST APIs and they call themselves the Firebase alternative too. But there are some differences between them.
| Appwrite | Supabase |
| Self-hosted | Hosted on the cloud and self-hosted |
| Uses MySQL and NoSQL databases | Use PostgreSQL database |
| Self-hosting pattern has advanced features | Self-hosting has basic features |
| Free packages | Offers paid packages |
Conclusion
Now, you have learned about appwrite, how to install it, and the service they provide. There are other services that you can use on appwrite. You can check their official documentation for a thorough guide on how to use appwrite. You can also join their developer community on discord